We use a bootable ISO in our environment to boot our VM’s to a specific set of PVS servers. This ISO will vary by region enforcing that each target device that boots will be directed to their closest PVS server.
However, we have 1 region that does not leverage this capability and this region was designed to utilize the PXE services of the Citrix PVS server’s. Occasionally, we encountered VM’s that will not boot and instead the console shows “PXE-E53: no boot filename received”
When I logged onto the Citrix PVS servers, I checked their services. Both services were reported as “Running”:
When I checked the event logs I did not see any errors in either the application log or the system log. Administrative events showed nothing out the usual either.
In order to confirm that the PVS service was actually listening, I executed
netstat -an
this showed me all the open ports the server was listening for and the processes tied to those ports. Since PXE is a UDP operation, I examined the UDP portion of the netstat output. 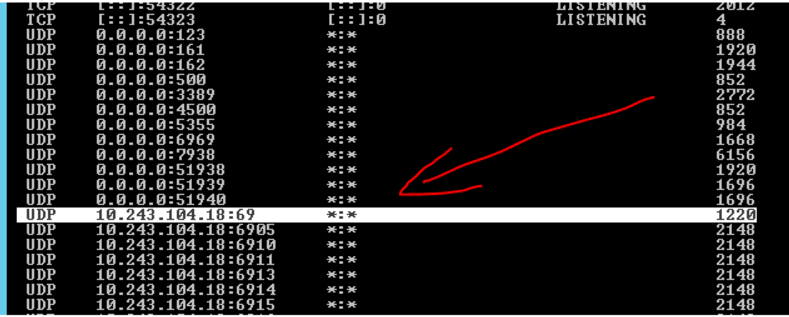
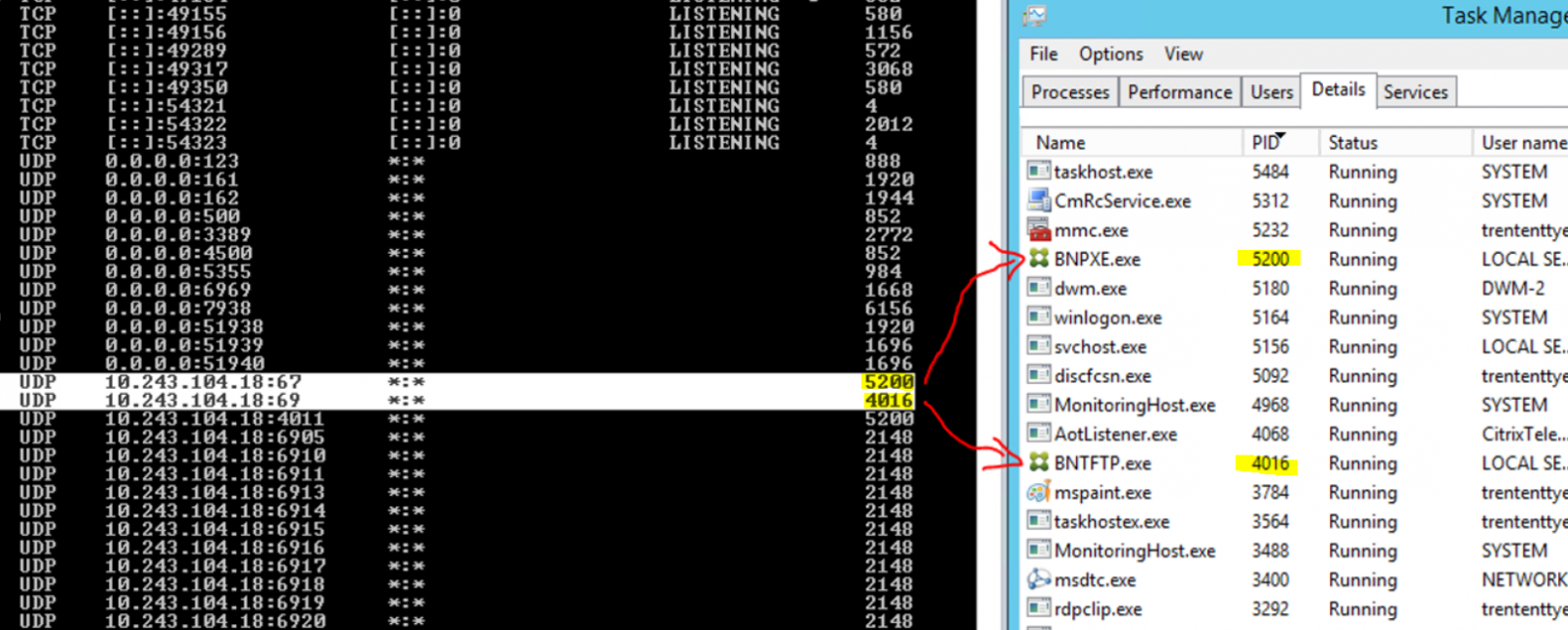
Port 69 is used by TFTP to transfer files, and port 67 is used by PXE. However, I only saw port 69, port 67 was no where to be found. I restarted the “Citrix PVS PXE Service”, reran netstat and confirmed that the PXE port was not listening and matched up the process ID to the proper services.
Restarting the failed target devices and they began to boot properly.
However, why did this fail in the first place? I read on the Citrix forums that the Citrix services can become unbound if the network is not available when the services are started. To test this I rebooted one the affected Citrix PVS servers. Sure enough, it came back up with port 67 not being monitored but the service in a ‘Running’ state. I wanted to see if I could capture the flow of communication from the network and when the service started so I used procmon and enabled “Boot Logging”.
Lo and behold, the procmon monitoring on startup added enough of a delay that the PXE service was bound consistently. Stopping the boot logging and the PXE service would start but fail to bind to the port.
So now this leads to a bit of a quandary. The delay seems to be in the milliseconds. I’ve considered a couple solutions for this issue.
- A startup script that checks to ensure both ports and restarts the proper service if one of the ports is not found.
- Change the service startup type to be “Automatic (Delayed Start)”. This delays the service by up to 2 minutes. This does mean that the PVS server will NOT be able to service target device boot requests during this window.
I think we’re going to go with option 2. The reason is we can apply this setting change via Group Policy Preferences. This ensures that if we any removal/upgrade of the PVS software this setting will get reapplied. And then we don’t have to worry about upgrading the OS and losing the startup script either or maintaining a script.
We’ve been affected by this a few times in the past, the fix has always been to restart the PVS server, but I managed to hit a window where the failure was happening consistently and managed to get this information.